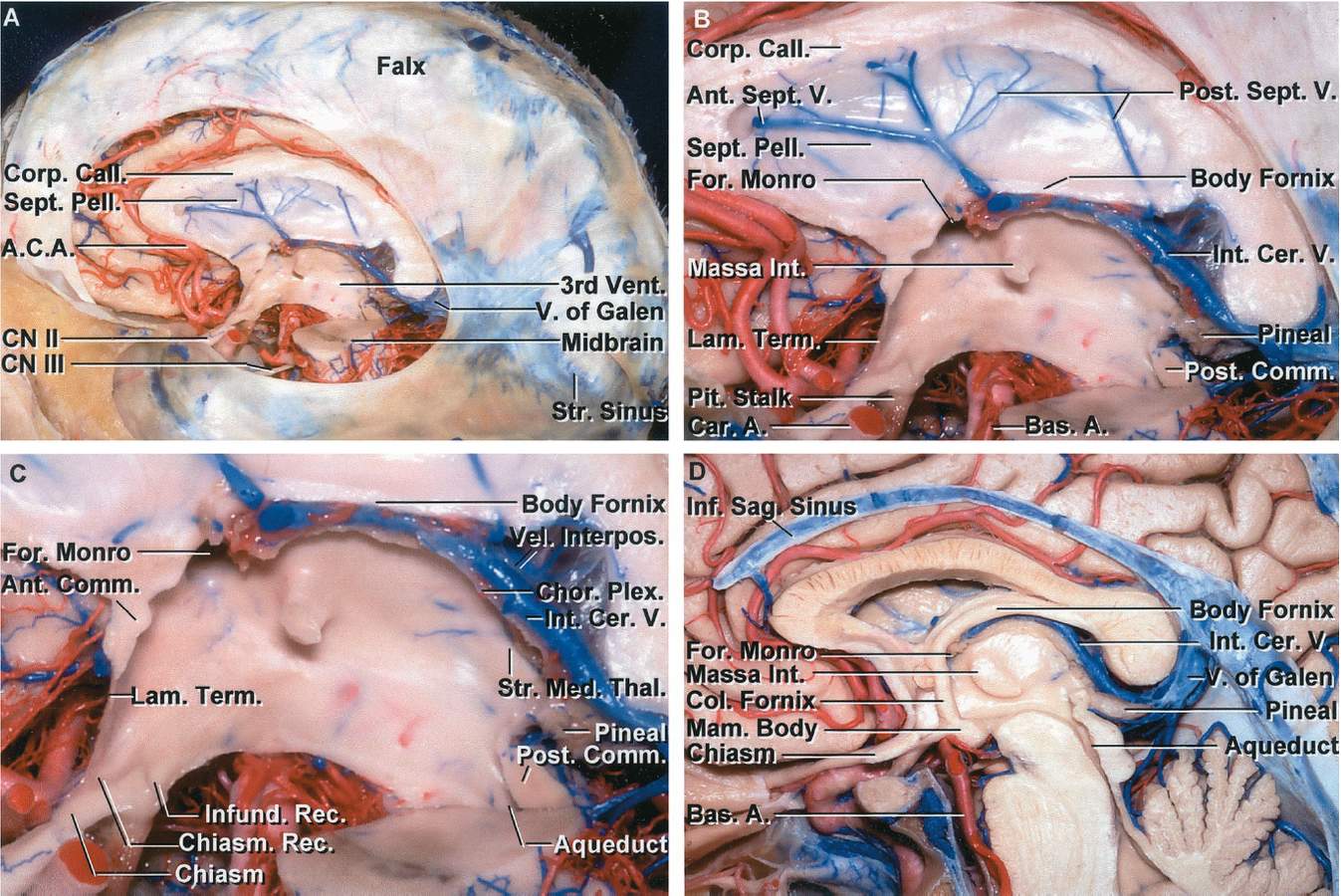
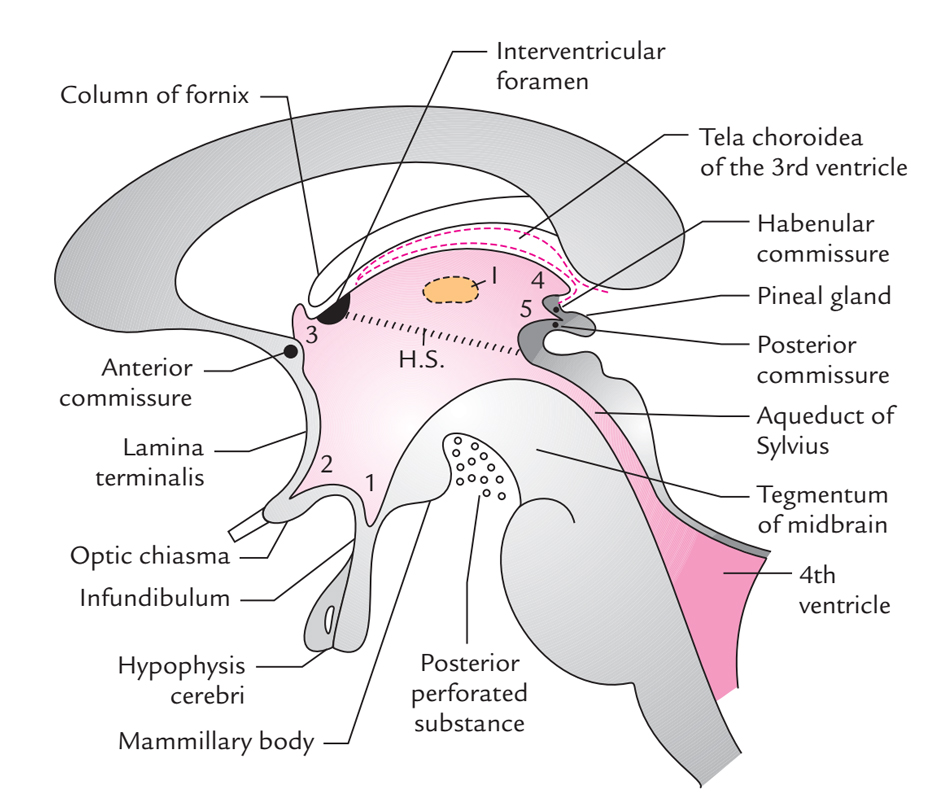
Floor and roof the floor is formed by the optic chiasma the tuber cinereum and the infundibulum the mamillary bodies the posterior perforated substance and the tegmentum of the midbrain.
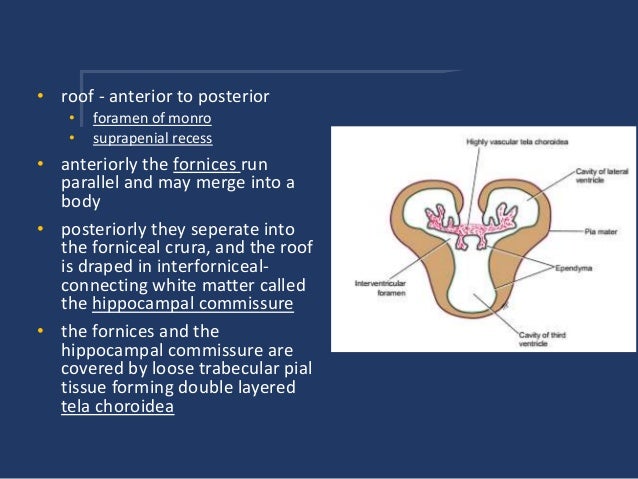
Posterior portion of roof of third ventricle.
Lamina terminalis roof.
This gap is called the transverse fissure.
The third ventricle has two lateral walls a roof a floor an anterior and a posterior wall.
It is a slit like space lying in the sagittal plane below the fornix and the corpus callosum.
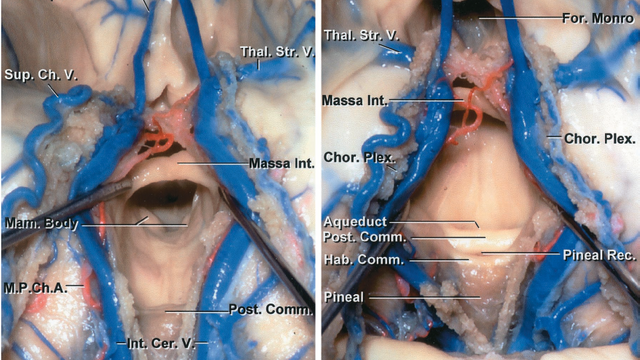
Its posterior portion houses the pineal gland and the habenular nuclei.
The obex is also a.
Which of the following cells do not have insulin receptors.
Which of the following structures lies in the posterior portion of the roof of the third ventricle.
Which of the following substances is a hormone stored and released by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
Formed by four layers.
This portion of the brain forms part of the roof of the diencephalon and covers the third ventricle.
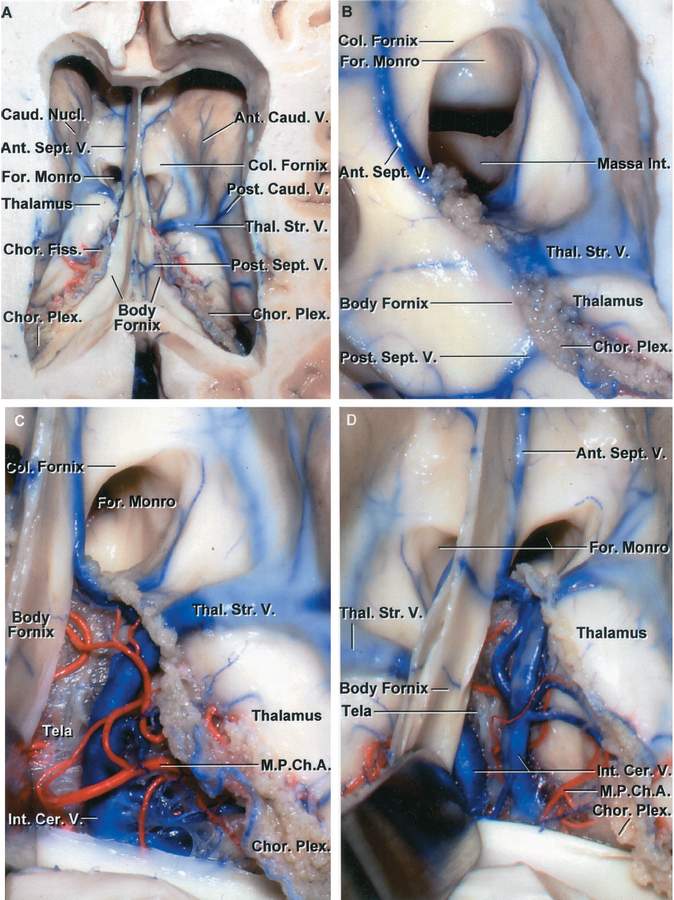
The anterior end representing theapex of the triangle lies near the right and left interventricular foramina.
Which of the following events is a result of.
The fourth ventricle has a roof at its upper posterior surface and a floor at its lower anterior surface and side walls formed by the cerebellar peduncles nerve bundles joining the structure on the posterior side of the ventricle to the structures on the anterior side.
The brain ventricle located in the diencephalon is the ventricle.
Its posterior end is broad and lies in the gap between the splenium above and the posterior part of the roof of the third ventricle below fig.
Its posterior portion houses the pineal gland and the habenular nuclei.
It is in the midline between the left and right lateral ventricles running through the third ventricle is the interthalamic adhesion which contains.
The third ventricle is a narrow midline cavity that communicates through the foramen of monro with the lateral ventricles and through the aqueduct with the fourth ventricle.
The third ventricle is one of the four csf filled cavities draining the lateral ventricle.
This portion of the brain forms part of the roof of the diencephalon and covers the third ventricle.
Like other ventricles the third ventricle has a cavity an anterior wall a posterior wall a floor a roof and two lateral walls.
The two thalami and superior portion of the hypothalamus.
The third ventricle is one of four connected fluid filled cavities comprising the ventricular system within the mammalian brain it is a median cleft in the diencephalon between the two thalami and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid csf.





:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/2138/QI1WvrA8l9WylteXMLXxw_Ventriculus_tertius_01.png)